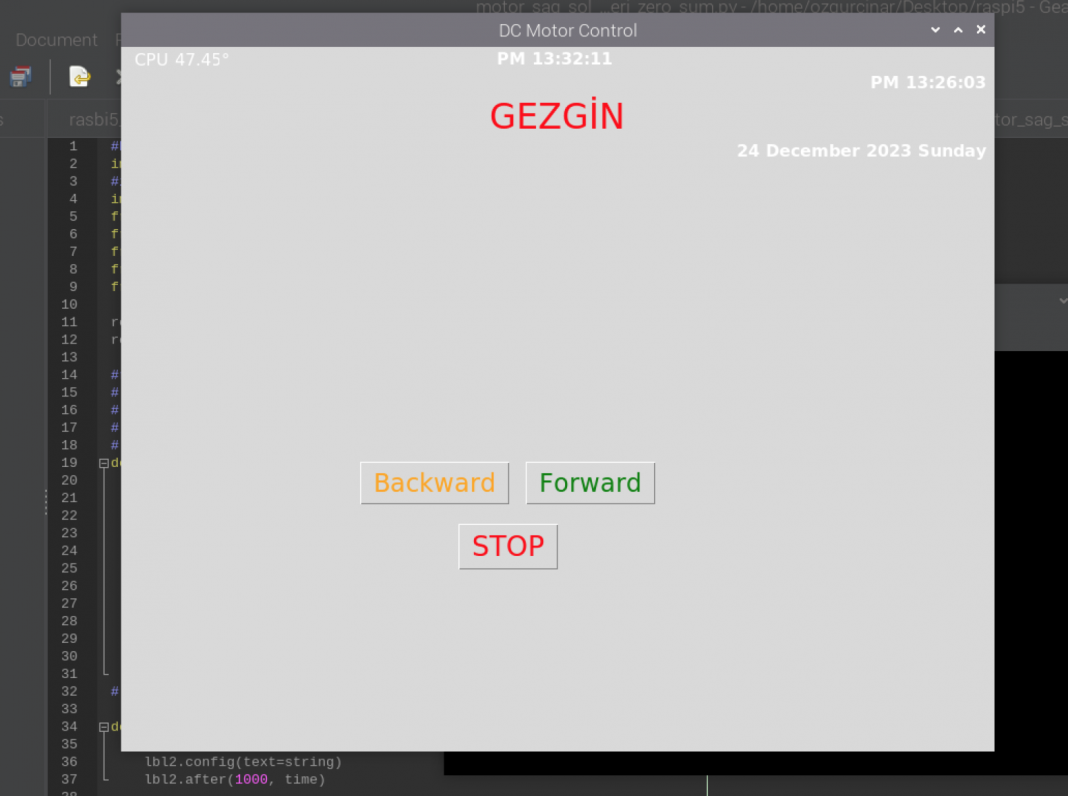
DC Motor Control With Raspberry Pi 5 and L293N
User interface has time & Date & CPU Temp & 3 Button labels.
#https://pinout.xyz/pinout/jtag
import gpiod as GPIO
#import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
from time import sleep
from time import strftime
from gpiozero import CPUTemperature
from gpiozero import Motor
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("DC Motor Control")
#root2 = Tk() #saat penceresi
# This function is used to
# display time on the label
# ozgurcinar@gmail.com
# mdemirkiran@hotmail.com
def cputemp():
lbl=Label(root, text=" CPU :", fg='white', font=("calibri", 12))
lbl.place(x=1, y=1)
cpu = CPUTemperature()
#relief=RAISED, label , 3boyutlu efekti
lbl=Label(root, text=cpu.temperature, fg='white', font=("calibri", 12))
lbl.place(x=50, y=1)
lbl.after(5000, cputemp) # update cycle
lbl=Label(root, text=chr(176), fg='white', font=("calibri", 12))
lbl.place(x=95, y=1)
# lbl.pack(anchor='sw', side='bottom') # satir satir
def time():
string = strftime('%p %H:%M:%S ')
lbl2.config(text=string)
lbl2.after(1000, time)
# Styling the label widget so that clock
# will look more attractive
lbl2 = Label(root, font=('calibri', 12, 'bold'),
#background='purple',
foreground='white')
# Placing clock at the centre
# of the tkinter window
#lbl2.pack(anchor='se', side='bottom')
lbl2.place(x=340, y=55)
root.geometry('1200x800')
lbl2.pack(anchor='center')
#mainloop() # ilk pencere buraya kadar .
# kapat diger pencerelere
#root3 = Tk() # bos pencere
def pdate():
string = strftime(' %d %B %Y %A ')
lbl4 = Label(root, font=('calibri', 12, 'bold'),foreground='white')
lbl4.config(text=string)
lbl4.place(x=340, y=5)
# root.geometry('1200x800')
lbl4.pack(anchor='ne', side='top')
def timess():
string = strftime('%p %H:%M:%S ')
lbl3.config(text=string)
lbl3.after(1000, time)
# Styling the label widget so that clock
# will look more attractive
lbl3 = Label(root, font=('calibri', 12, 'bold'),
#background='purple',
foreground='white')
# Placing clock at the centre
# of the tkinter window
#lbl2.pack(anchor='se', side='bottom')
#lbl3.place(x=340, y=5)
root.geometry('1000x300')
lbl3.pack(anchor='ne', side='top')
motor_R = Motor(forward=17, backward=18)
# GPIO pin tanimlamalari
motor_L = Motor(forward=23, backward=24)
# Motor durumlar
def forward():
motor_R.forward()
#sleep(4)
#stop()
def backward():
motor_R.backward()
#sleep(4)
#stop()
def stop():
motor_R.stop()
# Tkinter GUI
def create_gui():
lbl=Label(root, text="GEZGIN", fg='red', font=("calibri", 25))
lbl.place(x=340, y=25)
root.geometry('1200x800')
lbl.pack(anchor='center')
time()
pdate()
cputemp()
timess()
# Ileri hareket dugmesi
forward_button = tk.Button(root, text="Forward", command=forward,fg='green',font=("calibri", 18))
forward_button.place(x=390, y=400)
#forward_button.pack()
# Geri hareket dugmesi
backward_button = tk.Button(root, text="Backward", command=backward, fg='orange', font=("calibri", 18))
backward_button.place(x=230, y=400)
#backward_button.pack()
# Durdurma dugmesi
stop_button = tk.Button(root, text="STOP", command=stop, fg='red',font=("calibri", 20))
stop_button.place(x=325, y=460)
#stop_button.pack()
# GUI dongusu baslat
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_gui()